EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
 Fully half of the electricity used in the United States goes to power some 35 million electric motors that are larger than one horsepower and that annually consume over $90 billion worth of electricity. While electric motors are inherently efficient end-use conversion devices, the energy savings and lifecycle economics of high and premium efficiency motors simply can’t be ignored. But there is a dearth of information regarding the specifications, price, and availability of energy-efficient motors. To fulfill this information gap, the Washington State Energy Office created MotorMaster, a user-friendly software package that presents a wealth of information on high efficiency motors.
Fully half of the electricity used in the United States goes to power some 35 million electric motors that are larger than one horsepower and that annually consume over $90 billion worth of electricity. While electric motors are inherently efficient end-use conversion devices, the energy savings and lifecycle economics of high and premium efficiency motors simply can’t be ignored. But there is a dearth of information regarding the specifications, price, and availability of energy-efficient motors. To fulfill this information gap, the Washington State Energy Office created MotorMaster, a user-friendly software package that presents a wealth of information on high efficiency motors.
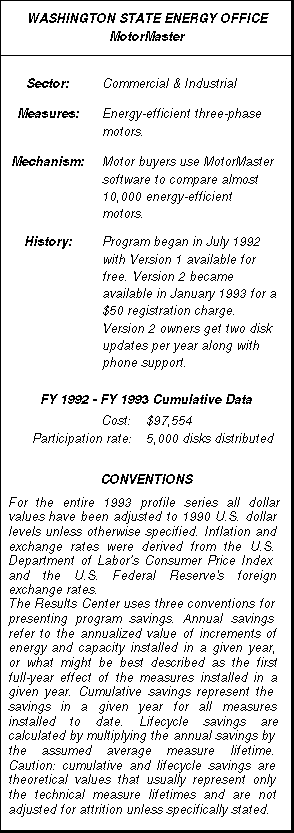
MotorMaster provides comparative information on three-phase motors and allows its users to review motor features such as enclosures available, efficiency at various loads, and price. The second version of MotorMaster, which has been available since January 1993, contains information on almost 10,000 motor models, including amperage and torque ratings, supplied and reviewed by 17 major motor manufacturers.
MotorMaster analyzes three general motor purchase scenarios. First, when a new motor is to be purchased, MotorMaster can compare the cost effectiveness of any two models. Second, when a motor fails, a decision needs to be made whether to rewind the motor or purchase a new one. MotorMaster compares the cost and efficiency of a new motor against repairing the old one. Third, there is the possibility of replacing an operating motor with a more efficient model.
MotorMaster targets a wide profile of users. Engineering firms can use the software to perform calculations for specific applications. MotorMaster helps mechanics faced with replacing equipment. Motor vendors can benefit greatly from the Version 2 MotorMaster disk because a filter is available which allows users to select what manufacturers’ products show up on the screen. Salespeople can print out sheets comparing the motors they have for sale.
MotorMaster can support utility motor rebate programs by identifying which models meet minimum efficiency requirements. MotorMaster contains a sample library of utility motor rebate programs which currently includes Pacific Gas & Electric, Consolidated Edison, Rochester Gas & Electric, BPA, Portland General Electric, and Puget Sound Power & Light. Data for additional rebate programs can be incorporated by the user, and rebate files can be easily created or modified.
Perhaps the most remarkable aspect of MotorMaster is the significance of the project in relation to its cost. The program has essentially been run by one individual, Todd Litman, with a total budget of less than $100,000. By January 1993 roughly 5,000 MotorMaster disks had been distributed though it is estimated that half of all people receiving the MotorMaster disk will pass it on to another user, resulting in at least 7,500 copies in circulation.
[CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD THE ENTIRE 15 PAGE PROFILE IN PDF FILE FORMAT]
This profile was produced by 

 Pacific/Utah Power, the electric generation and distribution divisions of PacifiCorp, is a forerunner in a new and innovative type of efficiency program in which customers repay the costs of their efficiency installations through monthly energy service charges on their electric bills. While the jury is still out on the effectiveness of this approach compared to more traditional rebate and other incentive programs, Pacific/Utah Power’s pioneering efforts with financing energy services for its customers is a model that is being closely watched around the country.
Pacific/Utah Power, the electric generation and distribution divisions of PacifiCorp, is a forerunner in a new and innovative type of efficiency program in which customers repay the costs of their efficiency installations through monthly energy service charges on their electric bills. While the jury is still out on the effectiveness of this approach compared to more traditional rebate and other incentive programs, Pacific/Utah Power’s pioneering efforts with financing energy services for its customers is a model that is being closely watched around the country. The Alaska Craftsman Home Program (ACHP) is a non-profit corporation that was formed through a cooperative arrangement between the University of Alaska Cooperative Extension Service, the State government, and the Alaska Homebuilders’ Association. The program’s goal is to improve the energy efficiency of new residential construction in Alaska by educating Alaskan builders and purchasers about the benefits of energy efficiency.
The Alaska Craftsman Home Program (ACHP) is a non-profit corporation that was formed through a cooperative arrangement between the University of Alaska Cooperative Extension Service, the State government, and the Alaska Homebuilders’ Association. The program’s goal is to improve the energy efficiency of new residential construction in Alaska by educating Alaskan builders and purchasers about the benefits of energy efficiency. Green Mountain Power launched its Small Commercial and Industrial Retrofit Program at an opportune time, just after an ice dam on the Winooski River caused the river to spill over its banks in the state capitol of Montpelier, flooding the town and causing severe hardship for small business owners. GMP’s door-to-door campaign promoting the Small C/I Retrofit program was most welcome, and the program quickly had its first 65 participants. By the end of 1992 the program had exceeded its participation goal for the year of 500 customers.
Green Mountain Power launched its Small Commercial and Industrial Retrofit Program at an opportune time, just after an ice dam on the Winooski River caused the river to spill over its banks in the state capitol of Montpelier, flooding the town and causing severe hardship for small business owners. GMP’s door-to-door campaign promoting the Small C/I Retrofit program was most welcome, and the program quickly had its first 65 participants. By the end of 1992 the program had exceeded its participation goal for the year of 500 customers.