EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
 In March 1988, the Lighting Research Center (LRC) was established within the School of Architecture at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Troy, New York. The LRC is the largest university-based research center for lighting in the United States. The center emphasizes lighting research and development, technology transfer, and education. The LRC has ties with other lighting laboratories and centers, and receives input from all sectors of the lighting, building, and utility industries.
In March 1988, the Lighting Research Center (LRC) was established within the School of Architecture at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Troy, New York. The LRC is the largest university-based research center for lighting in the United States. The center emphasizes lighting research and development, technology transfer, and education. The LRC has ties with other lighting laboratories and centers, and receives input from all sectors of the lighting, building, and utility industries.
Current LRC activities include the Partners program, the National Lighting Product Information Program (NLPIP), the Graduate Education in Lighting program, the Research and Development in Efficient Lighting program, the Research and Development in Human Factors program, the Technology Transfer program, and the Outreach Education program.
Research topics covered by the LRC include: lighting and safety, lighting and security, visibility of exit signs, illuminance levels, and people’s acceptance of efficient lighting technologies. The LRC also looks at the needs of DSM and energy conservation programs, as well as longer-term issues that relate to efficient lighting.
LRC expenditures for FY 1988 through FY 1992 total $6,686,200, with expenditures of $2,162,000 in FY 1992. Funding for the center comes from a diverse group of sources including government (44%), utilities (34%), manufacturers, associations, universities, and consulting firms.
The Lighting Research Center has helped to fill a critical information niche in the efficient-lighting industry, focusing its projects on areas where little information exists. A real emphasis has been placed on conducting the LRC as a business rather than a "typical" university-based research organization in order to avoid being cast as a group of "academics" whose work does not focus on everyday business needs. Perhaps the most unique feature of the LRC is its publication of product specific performance information, which other organizations either cannot or will not publish.
The staff of the LRC believes that it has greatly impacted the lighting manufacturing industry through its product performance reports which affect manufacturer sales, manufacturer marketing, and lighting specifier product selection.
[CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD THE ENTIRE 15 PAGE PROFILE IN PDF FILE FORMAT]
This profile was produced by

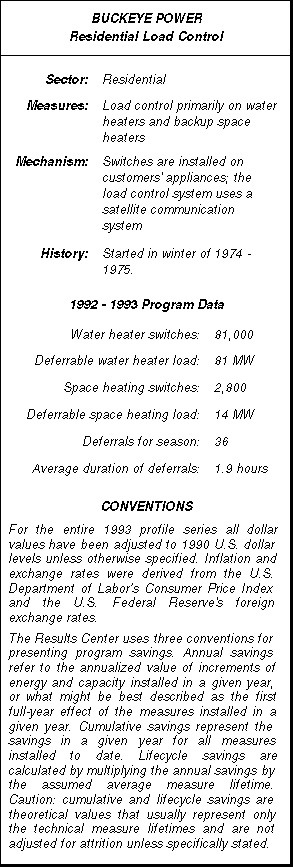 Buckeye Power’s Residential Load Control program is offered to the member consumers of each of its 27 member cooperatives. Through the program, 81,000 residential electric water heaters throughout the Buckeye service area may be controlled during peak demand periods. Additionally, approximately 2,800 residential electric space heating systems are controlled through the program.
Buckeye Power’s Residential Load Control program is offered to the member consumers of each of its 27 member cooperatives. Through the program, 81,000 residential electric water heaters throughout the Buckeye service area may be controlled during peak demand periods. Additionally, approximately 2,800 residential electric space heating systems are controlled through the program.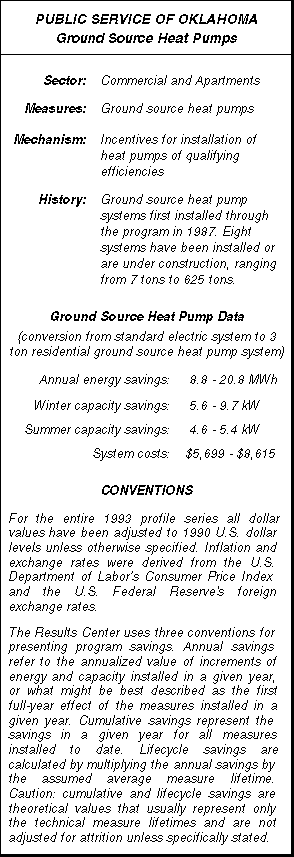 Jim Ezell of Public Service of Oklahoma notes that, "Ground source heat pumps are really a product of Oklahoma. While the technology can be applied across the United States and perhaps around the world, it has its genesis in Oklahoma." Thus it is fitting that this profile focuses on the PSO program and incorporates the national perspective by using detailed analytical work done by U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
Jim Ezell of Public Service of Oklahoma notes that, "Ground source heat pumps are really a product of Oklahoma. While the technology can be applied across the United States and perhaps around the world, it has its genesis in Oklahoma." Thus it is fitting that this profile focuses on the PSO program and incorporates the national perspective by using detailed analytical work done by U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.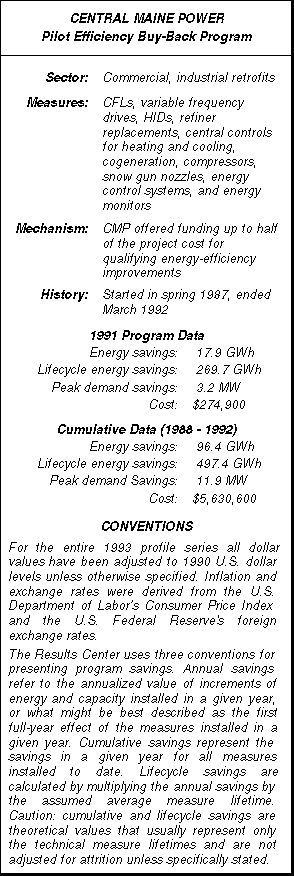 Central Maine Power’s Pilot Efficiency Buy-Back program (EBB) was implemented in the spring of 1987. CMP hoped to quickly achieve large energy savings by targeting its major commercial and industrial customers. Interested customers submitted proposals for improving the electric efficiency of their facilities. There were no requirements as to the types of measures installed. Savings requirements were very high. Proposed projects had to save a minimum of 500,000 kWh per year and shift (or reduce) winter on-peak demand by 500 kW. Qualifying projects received funding from CMP which could reach a maximum of half the project cost.
Central Maine Power’s Pilot Efficiency Buy-Back program (EBB) was implemented in the spring of 1987. CMP hoped to quickly achieve large energy savings by targeting its major commercial and industrial customers. Interested customers submitted proposals for improving the electric efficiency of their facilities. There were no requirements as to the types of measures installed. Savings requirements were very high. Proposed projects had to save a minimum of 500,000 kWh per year and shift (or reduce) winter on-peak demand by 500 kW. Qualifying projects received funding from CMP which could reach a maximum of half the project cost.