Environmental Resource Center, Destination Conserv. (inst'l-school retrofit/educational), Profile#82
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Destination Conservation (DC) is a school retrofit program that demonstrates a clever formula for energy and water savings. The program engages school principals, custodians, students, faculties, and their communities in a cooperative effort to gain incremental dollar savings which can then be used for more and more sophisticated retrofit measures. Conceived in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada, by staff at the non-profit Environmental Resource Center, the program is based on a three-year staged approach whereby no and low cost retrofits in Year 1 create savings that can then be applied to progressively more comprehensive efficiency measures in Years 2 and 3. Basic "lifestyle" changes in Year 1, such as turning off unneeded lights, create savings that can be applied to low cost retrofits, such as purchasing and installing occupancy sensors to control classroom lights, which in turn can create revenues for more capital intensive retrofits such as replacing incandescent lamps with compact fluorescents.
Destination Conservation (DC) is a school retrofit program that demonstrates a clever formula for energy and water savings. The program engages school principals, custodians, students, faculties, and their communities in a cooperative effort to gain incremental dollar savings which can then be used for more and more sophisticated retrofit measures. Conceived in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada, by staff at the non-profit Environmental Resource Center, the program is based on a three-year staged approach whereby no and low cost retrofits in Year 1 create savings that can then be applied to progressively more comprehensive efficiency measures in Years 2 and 3. Basic "lifestyle" changes in Year 1, such as turning off unneeded lights, create savings that can be applied to low cost retrofits, such as purchasing and installing occupancy sensors to control classroom lights, which in turn can create revenues for more capital intensive retrofits such as replacing incandescent lamps with compact fluorescents.
The DC "formula" for savings utilizes the abilities of three key players: DC, which facilitates the process and provides the expertise; the school district, which harnesses the collective energy of students and staff alike; and a corporate sponsor, which provides early capital for audits and trainings, and then later provides additional capital for comprehensive retrofits. Corporate sponsors, which to date have primarily been utilities, recoup all their money over time. A new program track, begun in early 1994, allows schools to move directly to capital intensive retrofits, which are generally subcontracted to regional firms, with their commensurate dollar savings in Year 1. In both tracks, the program enables schools to retrofit their facilities without any cash outlay and then provides schools with positive cash flow since their loan repayments are structured to be less than their monthly bill savings.
To date, 24 school districts in Alberta with over 220 schools have participated or are currently participating in the program. In Ontario and Saskatchewan, three school districts are participating, while British Columbia and New Brunswick each have two school districts involved in the program. In terms of savings, the DC program promotes comprehensive retrofits and works with schools to get systematic retrofits done at the lowest possible cost. The 87 participating schools in TransAlta Utilities’ service territory, for example, have saved an average of approximately 25% of their baseline utility bills. And while these energy savings are financially attractive to the schools, Destination Conservation also plays an important role in teaching schoolchildren about their role in protecting the environment and sustainable development by getting students integrally involved in the process.
[CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD THE ENTIRE 20 PAGE PROFILE IN PDF FILE FORMAT]
This profile was produced by


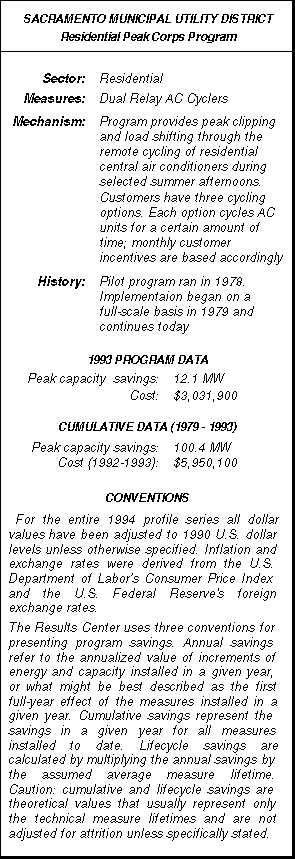 More than a decade before the Sacramento Municipal Utility District (SMUD) prematurely retired its Rancho Seco Nuclear Plant, ushering in a dynamic period of demand-side management, SMUD implemented its Residential Peak Corps program as a full-scale initiative. The program then, just as it is now, was intended to address Sacramento’s needle peaks which occur on summer days when temperatures climb above 100° F, sometimes for several days in a row.
More than a decade before the Sacramento Municipal Utility District (SMUD) prematurely retired its Rancho Seco Nuclear Plant, ushering in a dynamic period of demand-side management, SMUD implemented its Residential Peak Corps program as a full-scale initiative. The program then, just as it is now, was intended to address Sacramento’s needle peaks which occur on summer days when temperatures climb above 100° F, sometimes for several days in a row. Southern California’s Customer Technology Application Center (CTAC) represents a new wave in demand-side management for several reasons. The facility, fully one-acre in size and located just 30 miles east of Los Angeles, not only promotes energy-efficient technologies but provides industrial customers with critical services related to environmental compliance. Without CTAC, Edison may have lost several major accounts because of these customers’ inability to remain profitable while implementing costly pollution prevention technologies. CTAC has not only served to enhance Edison’s other DSM programs, and to provide customers with energy and money saving solutions, but serves as a critical economic development tool for Southern California.
Southern California’s Customer Technology Application Center (CTAC) represents a new wave in demand-side management for several reasons. The facility, fully one-acre in size and located just 30 miles east of Los Angeles, not only promotes energy-efficient technologies but provides industrial customers with critical services related to environmental compliance. Without CTAC, Edison may have lost several major accounts because of these customers’ inability to remain profitable while implementing costly pollution prevention technologies. CTAC has not only served to enhance Edison’s other DSM programs, and to provide customers with energy and money saving solutions, but serves as a critical economic development tool for Southern California.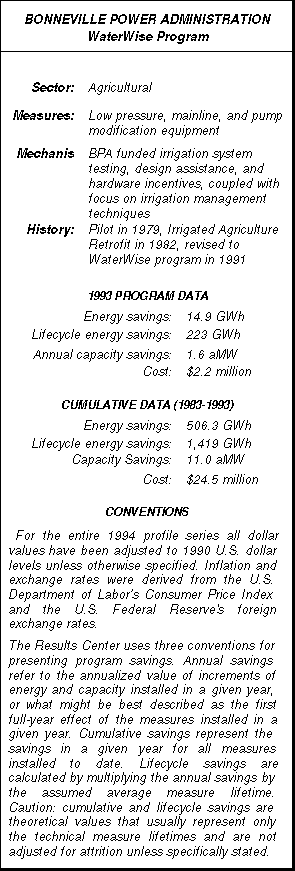 Bonneville Power Administration’s WaterWise program is an agricultural initiative that has evolved into a comprehensive effort that results in the triple benefits of energy and water savings and often increased crop yields thanks to the precision application of water. WaterWise dates back to 1979 when BPA first addressed irrigated agriculture’s energy use by developing a pilot program that focused on pump testing and evaluating farmers’ irrigation systems. A few years later BPA instituted the program on a regional basis and added incentives to the program for equipment retrofits. Then in 1991 these early programs were dramatically ramped up to create WaterWise, a program that addresses the needs of farms of varying sizes. In its current form, WaterWise is implemented by 39 retail utilities within BPA’s service territory.
Bonneville Power Administration’s WaterWise program is an agricultural initiative that has evolved into a comprehensive effort that results in the triple benefits of energy and water savings and often increased crop yields thanks to the precision application of water. WaterWise dates back to 1979 when BPA first addressed irrigated agriculture’s energy use by developing a pilot program that focused on pump testing and evaluating farmers’ irrigation systems. A few years later BPA instituted the program on a regional basis and added incentives to the program for equipment retrofits. Then in 1991 these early programs were dramatically ramped up to create WaterWise, a program that addresses the needs of farms of varying sizes. In its current form, WaterWise is implemented by 39 retail utilities within BPA’s service territory.